The purpose of all activities in education is to lead the child to better learning. How can we use robots to support education and especially special needs education? In this blog we dive into the research at EPFL, CHILI lab, with social robotics and post-doctoral researcher Dr. Barbara Bruno to hear about their projects with QTrobot and what feedback her researcher team has!
Computer Human Interaction in Learning and Instruction – CHILI lab
Let’s start with presenting EFPL and CHILI lab – who are they and what do they do? At EPFL, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne, the researchers of CHILI lab study collaborative technologies to improve learning and problem-solving. The aim of the CHILI lab is to integrate Human-Computer interaction and learning sciences. With a special focus on finding solutions to problems in learning, teaching and instruction, the studied solutions are always tested in classroom setting. Methods used at the CHILI lab include amongst others eye-tracking and integration of robotics in school- and home environment.
The research themes at CHILI lab are divided into three categories: modest computing, classroom orchestration and signal level computing. Next, we go further in detail into two current research projects of the CHILI lab: ANIMATAS and JUSThink projects and CoWriter – iReCHeCk.
Robots for computational thinking
A robot’s capabilities of mutual modeling can make it important and beneficial for learning. Can robots be used to convey new knowledge to children? Can robots support education and help especially children with special educational needs to learn better?
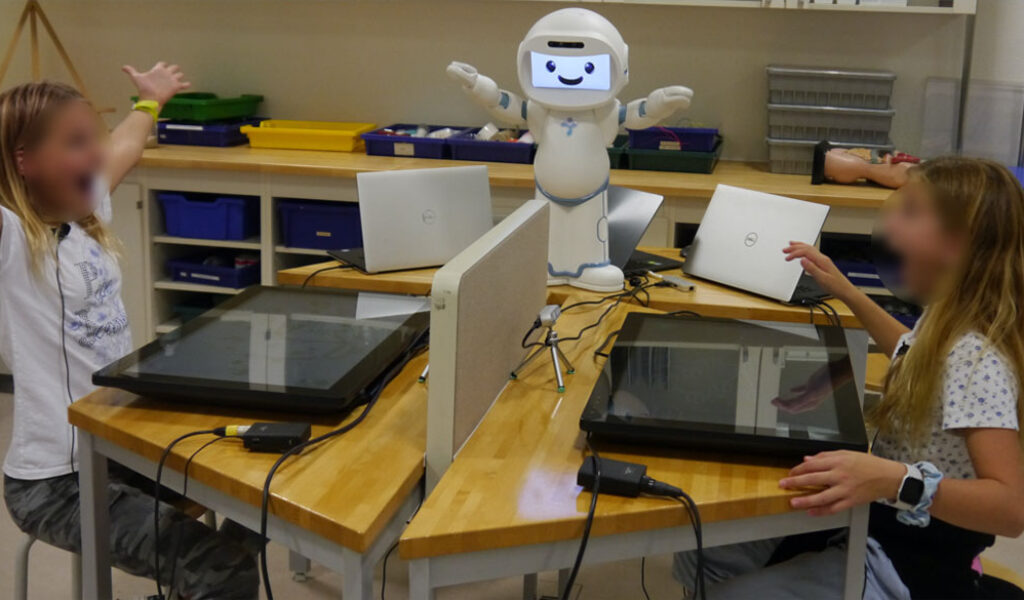
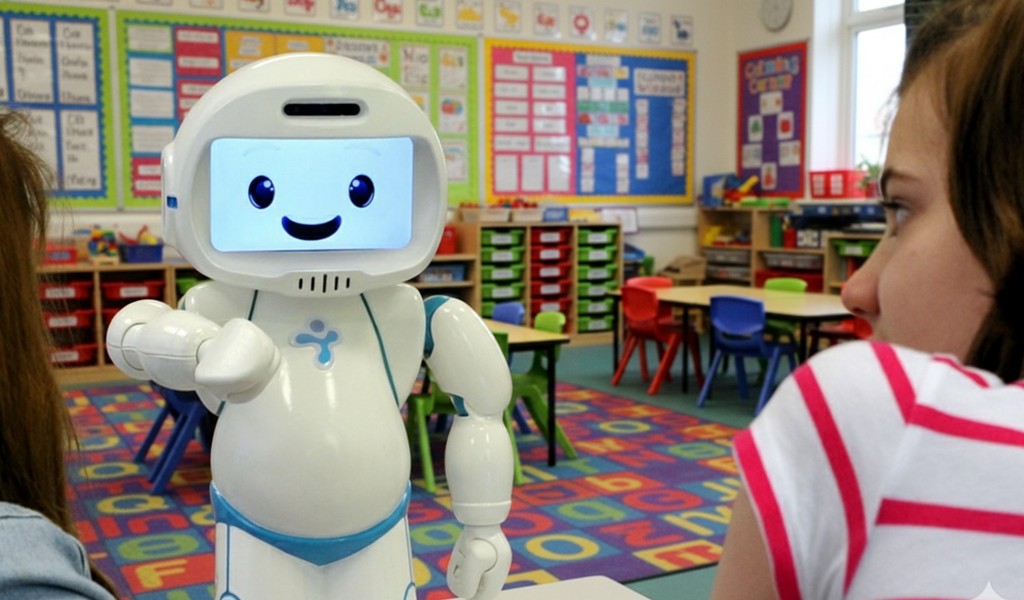
JUSThink is a research project striving to improve children’s computational thinking by practicing algorithmic reasoning with and through graphs. In practice, the research involves children working on various exercises with the assistance of a small tangible robot or a humanoid robot, such as QTrobot. The exercises are done under surveillance of an observer.
Working as a mediator in different exercises, the humanoid robots are evaluated for the use of conveying new knowledge to children in different activities. The robot’s presence is also evaluated from a motivational perspective, whether the presence of the robot itself provides motivational support and guidance. As a part of this study, collaboration between children with or without robot participation is evaluated. This leads to the question if a robot can enhance two people working together to improve collaboration between peers and improve learning? How can the robot take the attention of the children and use it to support them in their learning?
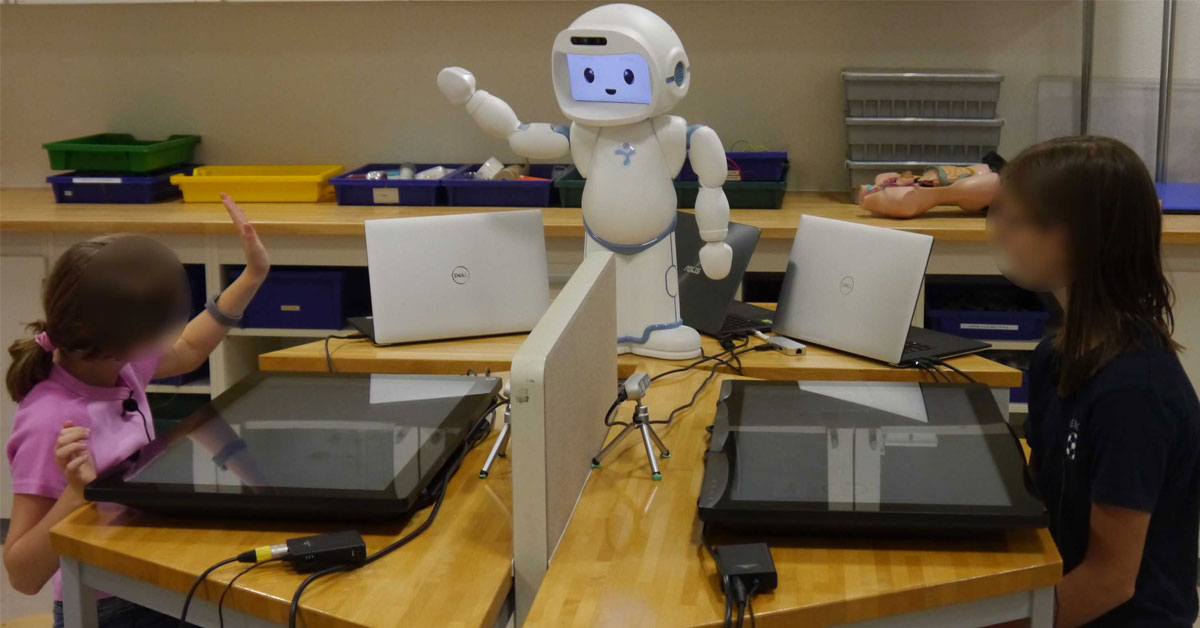

Can QTrobot convey computational thinking skills to children?
Many times, when a robot is part of an activity, it can capture the full attention of the children. In this study, the aim is to see how the robot can direct the attention of the children to support them in their learning process. QTrobot played a central role in the JUSThink research project. On one hand, the robot is used both as a mediator to improve collaboration of two children to support their learning and engagement. On the other hand, QTrobot is used as a direct collaborator working with one child, for the robot to see how the child understands the exercise and solve any potential misconception that the child might have.

The role of QTrobot in the JUSThink research project
Created as a collaborative game, in this research project children build a railway network between gold mines around Switzerland. QTrobot acts as the CEO of a gold mining company, providing the tasks and the instructions, to help the children build the railway network. In the first part of the project, QTrobot is a passive participant, being present, but not actively helping the children. In a latter part, QTrobot is actively participating to help the children, giving suggestions and discussion starters for the participating children, prompting them to reflect and to speak with each other.
For conducting the JUSThink research project, in total 100 children from two different schools participated in the tests and activities. Results show amongst others that the robot’s presence in the study setting of two children has a positive impact on their learning, even when only vaguely interfering in the tasks. Observation and assessment of how the children learn and behave during the educational activities also show that the more the children are involved in the activities, the more they learn. The findings of the studies in the JUSThink build a model, which is used to adapt the behaviour of the robot in different research contexts such as engagement and mutual modelling, in an educational setting, to improve learning.
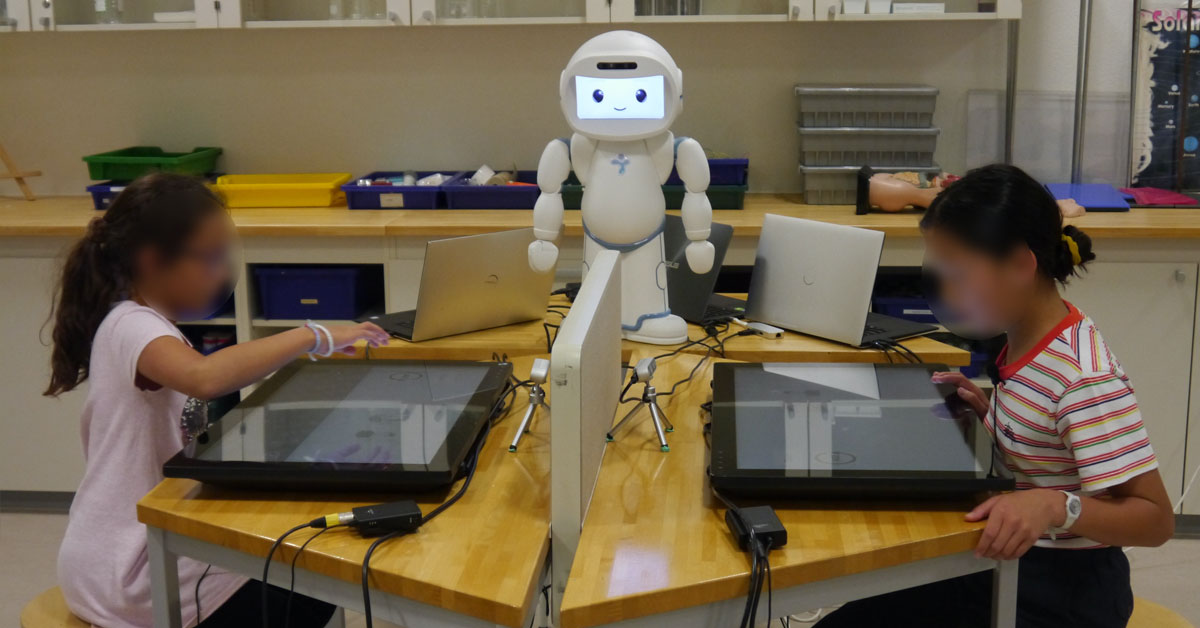

ANIMATAS – aim to establish a leading European Training Network
The JUSThink project, is a part of the ANIMATAS research project of the CHILI lab. The ANIMATAS project aims to establish a leading European Training Network for “development of a new generation of creative and critical research leaders and innovators who have a skill-set tailored for the creation of social capabilities necessary for realising step changes in the development of intuitive human-machine interaction (HMI) in educational settings”.
The aim is to be achieved via a transnational network of universities and industrial partners, combined with integrating key methods from different research domains; social robotics, embodied virtual characters, social and educational sciences. Through the European Training Network important knowledge flows from academia into the marketplace, strengthening the capacity of research and innovation in Europe and improving existing, as well as creating new potential products in intuitive human-machine interaction. Learn more about the Animatas project here.
Robots support education – improving handwriting skills
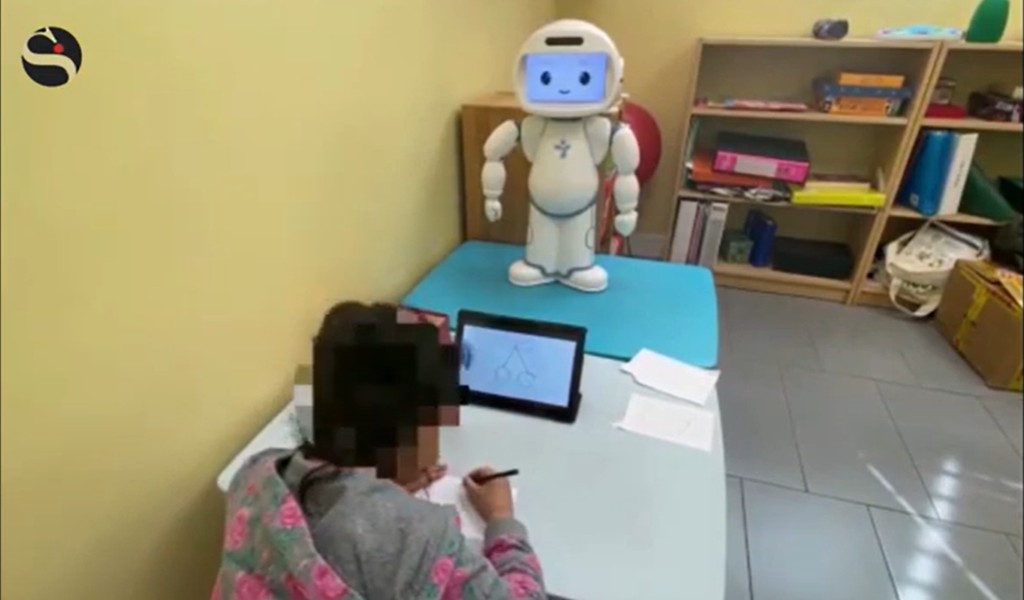
Handwriting is one of the basic skills for children needed for many basic skills for learning different subjects such as mathematics, science, languages and more. Having difficulties in handwriting can have a big impact on the self-esteem of a child and can lead to tough long-term consequences later in their life. In CHILI lab’s CoWriter Project and its follow-up iReCHeCk, the aim is to use the interaction between the robot and the child, reversing the perspective towards a learning by teaching paradigm to empower the child and increase their motivation and engagement to keep on practicing more. In this case the aim is to improve the child’s handwriting skills by having the child teach the robot how to write, helping the child be more engaged and therefore practice more.

Can QTrobot be used to improve handwriting skills?
Helping children exercise handwriting with the help of a person is very costly and resources are scarce. In the CoWriter Project and its follow-up iReCHeCk, Dr. Bruno and her research team study whether you can make the robot interact autonomously and increase or decrease use of a robot according to child’s and therapist’s need. This study also touches upon the relation and correlation between posture and handwriting, if it exists, and how it could be monitored by QTrobot. The robot could for example prompt breaks with physical exercises to overcome difficulties in handwriting and overcome motivational difficulties.
According to their studies, QTrobot has proven to be effective for children to approve their solutions and the correctness of their solutions. Robots can be very useful in education and provide astonishing results! Learn more about the CoWriter Project and iReCHeCk projects here.
How does QTrobot perform in research? Use case & testimonial of QTrobot – EPFL
Social robotics researcher and post-doctoral researcher Dr. Barbara Bruno has been using QTrobot in various research projects with her PhD students. As described above, the research projects conducted by the CHILI lab are often complex and need a robust solution to work for long days of study and evaluation.
Dr. Bruno compares QTrobot to other robots used in research, as she explains that it often happens when dealing with with social robots in research that they break and the entire research and team is affected by the fact that a hardware failure prevented the experiment from going as it should have done, and therefore it prevented your work. “Being responsible for making sure that my PhD student can can do their research, the fact that this robot never breaks is wonderful because it means that we can really test out our research and their research in the in the experiments“, says Dr. Bruno.
In their research projects, the team used many of the built-in features of QTrobot such as;
- Wi-Fi connectivity
- Camera for posture related information
- Facial expressions and speech
- Face recognition
- Skeleton tracking
- …and more!
“It’s rich and robust and I don’t think I could ask for anything better!”
About LuxAI and QTrobot
LuxAI is the founder, developer, and manufacturer of QTrobot and distributes QTrobots to countries around the world. QTrobot platform for research and development combines the best-in-the-market hardware components with a friendly design. QTrobot is a robust platform suitable for intensive working hours and multi-disciplinary research projects on social robotics and human-robot interaction. That makes QTrobot the ideal companion for researchers and developers in the field of social robotics.
QTrobot is a humanoid social robot with extensive capabilities to be used for research and development. QTrobot is a helpful tool in delivering best practices in child education, especially for children with autism and special educational needs. Being a robust platform with extensive built-in features, QTrobot can be used in many ways to support education and conducting research projects.