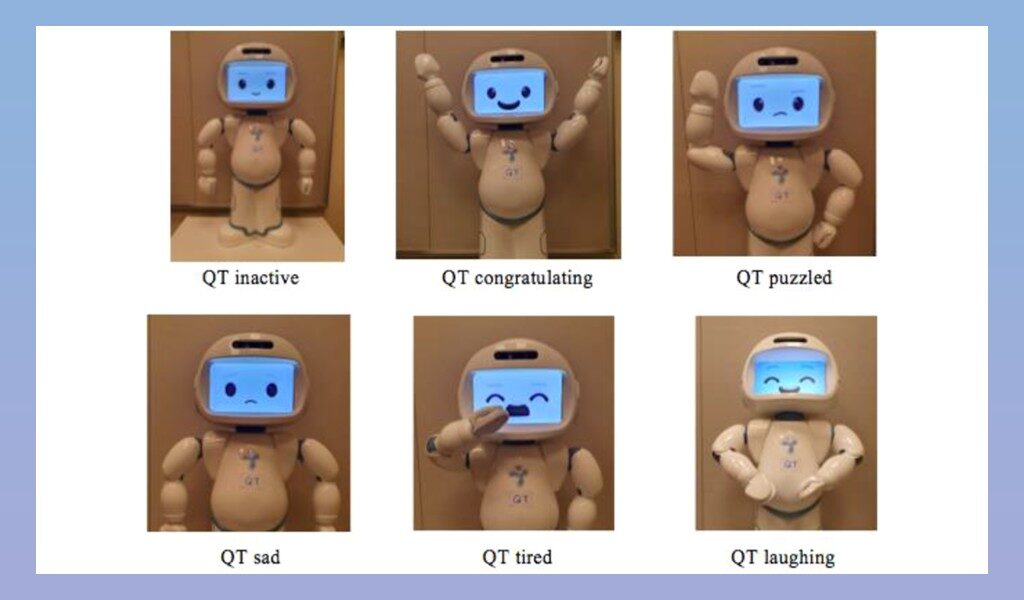
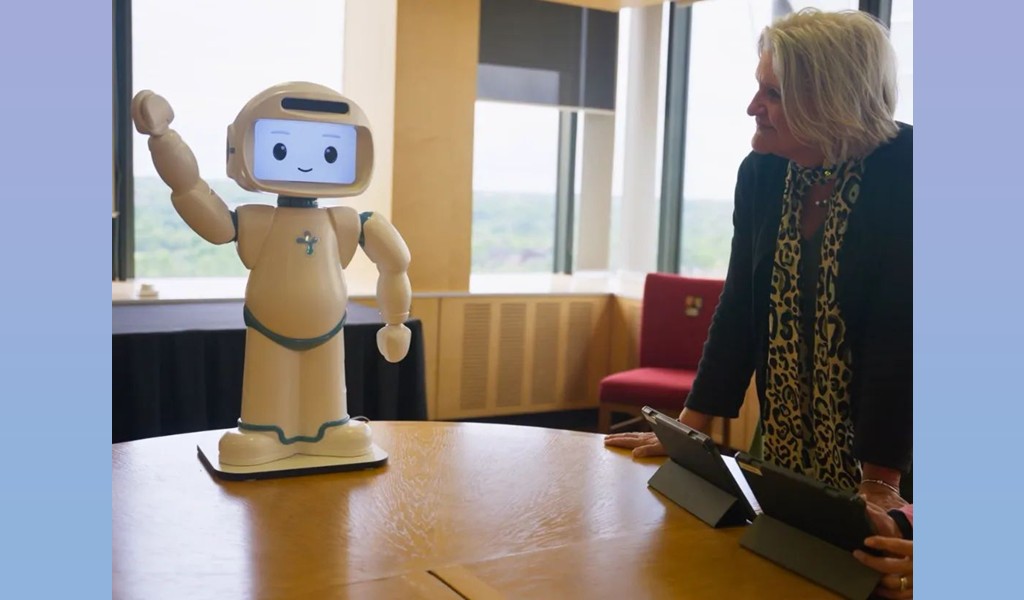
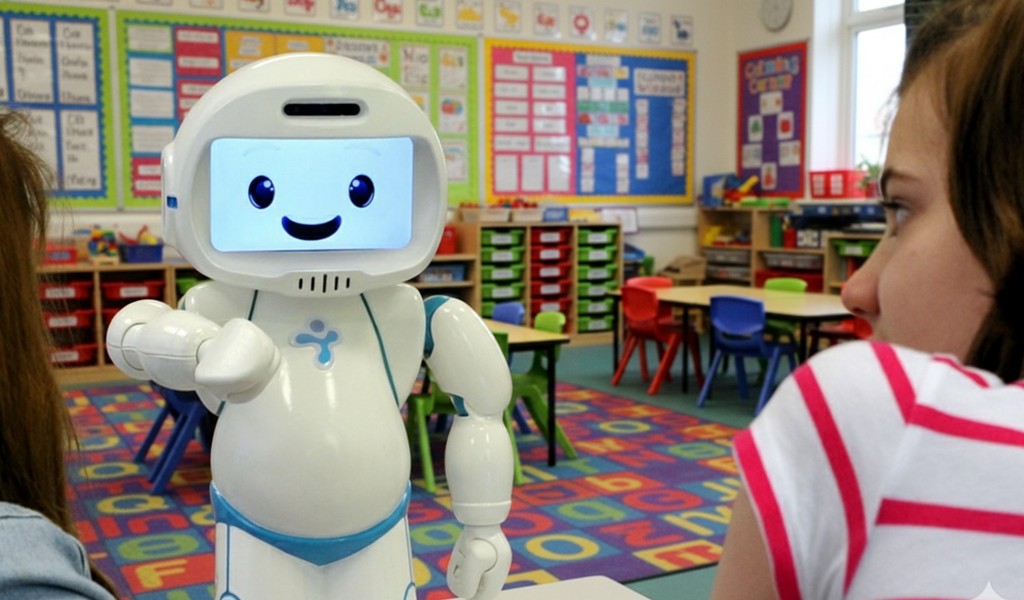
A recent study conducted in the Sorbonne University published in the International Journal of Social Robotics explored the impact of using QTrobot, operated through the R2C3 Wizard-of-Oz interface, in group social skills therapy sessions for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD).
The results highlight areas where QTrobot notably enhanced children’s social participation — pointing to its growing potential as a valuable tool in autism support programs.
Hypothesis
The researchers proposed that integrating QTrobot into social skills groups could:
Increase children’s social engagement, specifically initiations of interaction.
Support group-based autism interventions without disrupting or diminishing the effectiveness of traditional therapies.
They also wanted to test the feasibility and usability of the R2C3 interface for therapists operating the robot during live sessions.
Participant Recruitment and Group Formation
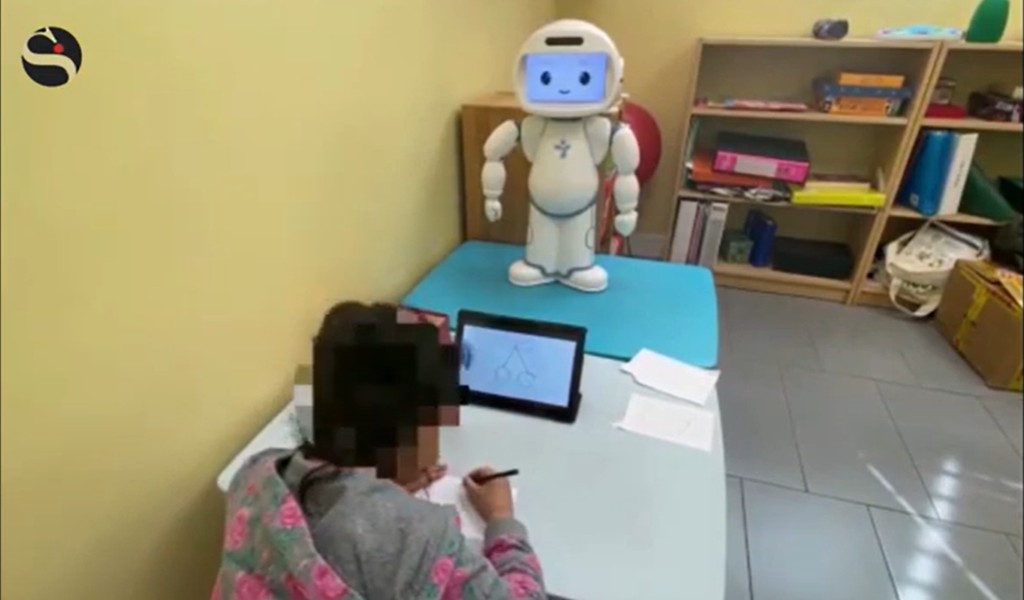
Six children were recruited from the outpatient unit of the Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Department at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital to participate in the study. Uniquely, the sample included four girls and two boys, differing from most autism studies where males typically make up 67% to 100% of participants.
To be eligible, participants needed to meet the following inclusion criteria:
A confirmed diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), validated by either the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R) or the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Second Edition (ADOS-2).
Age between 6 and 11 years.
No prior participation in a social skills group (SSG) intervention as part of their therapeutic care.
Consent provided by at least one
Outcome Measures
The study measured the robot’s impact by tracking:
ADOS-2 Scores: Changes in autism-related social and communication behaviors.
Social Initiations: How often children actively started interactions (a key skill that is typically challenging for children with ASD).
Social Responses: How often children responded to prompts from peers or adults.
DICTI Evaluation: Assessment of the robotic interface’s usability and ease of integration into therapy.
Data were collected during therapy sessions both with and without QTrobot to make direct comparisons.
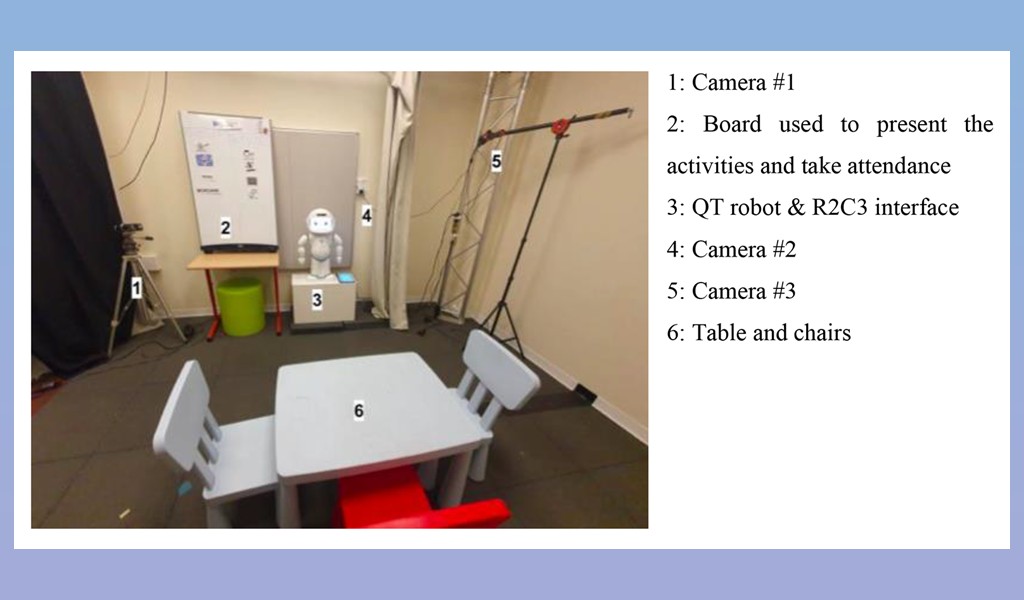
Experiment set up
Key Findings: Where QTrobot Made a Real Difference
1. Significant Increase in Social Initiations
One of the most important findings was that children initiated social interactions much more frequently when QTrobot was present and active.
This suggests that QTrobot successfully acted as a social catalyst — encouraging children to start interactions, which is often one of the hardest skills for them to develop.
Notably, the boost in initiations was especially strong in early sessions, indicating that QTrobot had an immediate positive effect on engagement.
2. Creating a Low-Pressure Social Environment
QTrobot provided a predictable, non-judgmental social partner, making it easier for children to engage without feeling overwhelmed.
This supports previous findings that children with autism often find interactions with social robots less stressful than interactions with unpredictable human partners.
Children appeared more comfortable and confident practicing communication when interacting with QTrobot, helping to lay the groundwork for broader social skill development.
3. Enhanced Group Dynamics
Therapists observed that QTrobot acted as a pivot of attention within the group — helping to structure activities and focus children’s attention in a dynamic but controlled way.
Even though direct social responses did not significantly improve during the study, the structured interaction patterns facilitated by QTrobot promoted more sustained engagement during group sessions.
Summary of Results
In summary:
QTrobot significantly increased social initiations among children with autism during therapy sessions.
Children engaged more readily and appeared more comfortable interacting in a group setting when QTrobot was active.
Further improvements to the control interface are needed to better integrate the robot into natural conversations.
Future studies with larger groups are recommended to validate and build on these promising results.
Overall, QTrobot demonstrated strong potential as an innovative tool to enhance social engagement and support early communication development for children with autism in group therapy settings.
Reference:
Bettencourt, C., Grossard, C., Zou, J., Segretain, M., Bree, M., Pellerin, H., Anzalone, S.M., Chetouani, M. and Cohen, D., 2025. Investigating the Feasibility of a Wizard-of-Oz Robotic Interface (R2C3) in a Social Skills Group for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. International Journal of Social Robotics, pp.1-17.
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12369-025-01243-4