Abstract:
Researchers recognize that communication is vital in human life, serving five major goals: informing, expressing feelings, imagining, influencing, and meeting social expectations. However, individuals with Neurodevelopmental Disorders (NDD) often find communication challenging. NDD affects 0.4% to 3% of the global population and is characterized by early-onset deficits of varying severity in personal, social, academic, or occupational functioning.
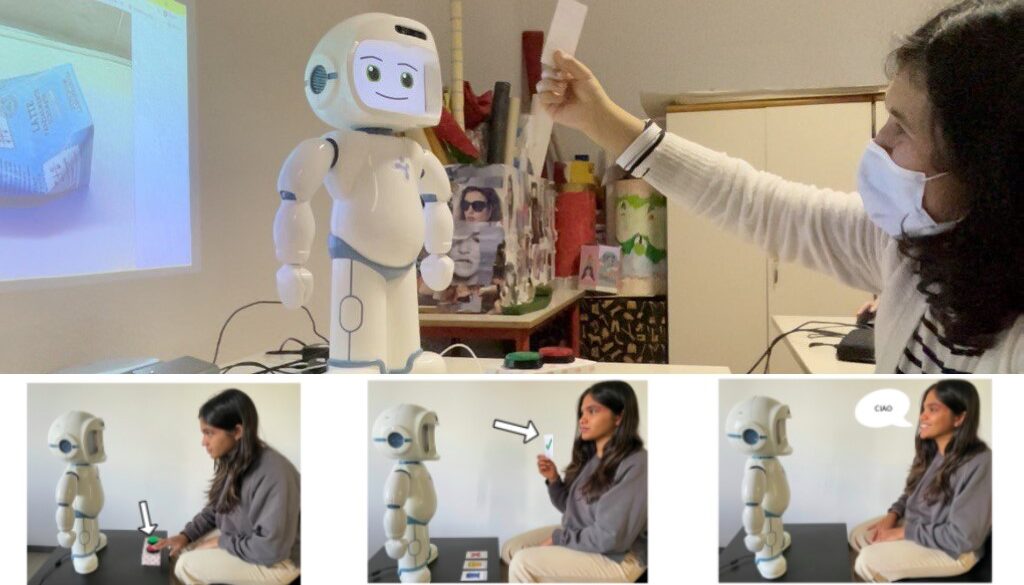
Over the years, numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of socially assistive robots in therapeutic settings. Building on this, the researchers conducted an exploratory study, developing a reinforcement social activity using QTrobot, allowing participants to interact through different modalities: voice, cards, and buttons. The research aimed to determine the most suitable interaction paradigm for individuals with NDD when interacting with a robot and to identify an efficient way to implement this type of interaction.
To address the first question, the researchers employed qualitative methods, including focus groups, observations, and surveys, involving 29 participants from two social educational centers: “Fraternità e Amicizia” and “CSE Collage.” For the implementation, they integrated behavior trees using the Python library, pytrees, into an existing open-source framework for human-robot interaction, HARMONI. This combination facilitated the development of an efficient activity that leveraged the strengths of both approaches.
The research highlights that combining different communication paradigms can enhance interaction between individuals with NDD and robots, making the engagement more effective. The gathered results indicate that participants enjoyed activities with the robot, with cards being the preferred interaction paradigm.
Reference: